Codabar
Codabar is a linear barcode symbology developed in 1972 by Pitney Bowes Corp. It and its variants are also known as Codeabar, Ames Code, NW-7, Monarch, Code 2 of 7, Rationalized Codabar, ANSI/AIM BC3-1995 or USD-4. Although Codabar has not been registered for US federal trademark status, its hyphenated variant Code-a-bar is a registered trademark.
Codabar was designed to be accurately read even when printed on dot-matrix printers for multi-part forms such as FedEx airbills and blood bank forms, where variants are still in use as of 2007. Although newer symbologies hold more information in a smaller space, Codabar has a large installed base in libraries. It is even possible to print Codabar codes using typewriter-like impact printers, which allows the creation of many codes with consecutive numbers without having to use computer equipment. After each printed code, the printer's stamp is mechanically turned to the next number, as for example in mechanical mile counters.
Codabar is a linear, symbology barcode that represents data using a series of bars and spaces of varying widths. It was developed in 1972 and is commonly used in libraries, blood banks, and other similar applications.
Codabar is capable of encoding the digits 0-9, as well as the characters $, +, -, ., /, and :. Unlike most other barcodes, Codabar does not include a checksum digit by default, which means that the data encoded must be read accurately for the entire barcode to be readable. Codabar barcodes are also self-checking, meaning that small variations in the print quality of the barcode will not affect its ability to be read by a barcode scanner.
There are also four different start and stop characters defined. These start and stop characters are used as A, B, C, and D. They are only valid at the beginning and end of the code. They can be used to carry additional information.
Codabar Barcode Overview
Codabar is a discrete and efficient barcode symbology with a maximum data length of 16 characters. In addition, this bar code type is also known as Codeabar, ABC Codabar, Ames Code, NW-7, Monarch, Code 2 of 7, Rationalized Codabar, Uniform Symbology Specification Codabar, USS Codabar ANSI/AIM BC3-1995 and USD-4.
Codabar is usually used in libraries, US blood banks, and the package delivery industry. Apart from those fields, it is also applied to photo labs, on FedEx airbills, and various information processing applications.
Codabar Barcode Structure
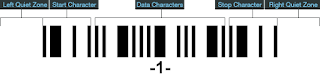
A Codabar symbol is made up of six parts: left quiet zone, start character, inter-character space, data characters, stop character and right quiet zone. Furthermore, each Codabar symbol character is comprised of seven elements: four bars and three spaces, among which two or three elements will be wide, while the rest will be narrow.
Codabar Barcode Encoding Data
The encodable data of Codabar bar code includes the following three aspects:
Ten Digits: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9;
Six symbols: - (Dash), $ (Dollar), : (Colon), . (Point), / (Slash), + (Plus);
Four letters: A, B, C, or D used as Start and stop characters.
Codabar Barcode Checksum Calculation
Codabar is a self-checking barcode, but there is no check digit defined as one part of the Codabar symbol structure. However, some specific industries, especially libraries, have their own checksum specifications.
Codabar Introduction
This page concerns basic information of Codabar, as well as its generating and printing components.
This part talks about the Codabar barcode. It is a discrete, self-checking symbology which is also known as Codeabar, Ames Code, NW-7, Monarch, Code 2 of 7, Rationalized Coda bar, ANSI/AIM BC3-1995 or USD-4. It is used by U.S. blood banks, photo labs, and on FedEx airbills.
Codabar is a self-checking barcode that is designed to be read on printed forms, especially from dot matrix printers. Its typical uses have include Fed-Ex packages and blood bank forms. In many ways, the Codabar code has become outdated, as newer code forms now allow a much larger amount of information to be contained in a much smaller space. However, the Codabar is not yet obsolete, and is still in use in libraries and several other organizations.
Specifications: A Codabar barcode consists of up to 16 different numeric characters, plus an optional 4 more letter characters which are used to designate the beginning and the end of the code. The order the letters are placed in designates what the barcode is being used for: library, blood bank, photo lab, etc. Since Codabar is self-checking, a check number at the end is not necessary, though some organizations choose to employ one anyway.
Advantages: Codabar is large and clearly spaced, making it easy to scan, even when printed by a standard printer. The code is also self-checking, which eliminates errors in entering in the code.
Disadvantages: As previously mentioned, Codabar is quickly going out of style, and being replaced by other, more efficient product identifiers.
Easily generate Codabar barcodes as a font in many applications.
Supplied with several normal and human-readable versions.
Multiple font types are included in the package, such as Digitally Signed TrueType, OpenType, PostScript, and PCL fonts.
Examples are provided for FileMaker®, OpenOffice, Microsoft® Word, Excel, Access, and SAP® Crystal Reports.
Compatible with 32 and 64-bit Windows®, Mac® OS, Unix, Linux, and mobile devices including iOS, Android, and .NET Compact Framework.
Supports Rationalized Codabar, USD-4, NW-7, 2 of 7 Code, and other specifications based on the Codabar barcode symbology.

Comments
Post a Comment